In the rich tapestry of Egyptian mythology, where gods and goddesses reign supreme, Shed emerges as a distinctive figure. Unlike the pantheon of well-known deities like Ra, Osiris, or Isis, Shed holds a unique place as a savior deity, often depicted as a young prince or a hunter. Revered in later periods of Egyptian history, Shed’s role transcends the boundaries of mere myth, symbolizing protection and salvation. Known colloquially as the “Savior,” he was invoked especially for safeguarding individuals against perils and evil forces. Shed’s portrayal as a defender against wild beasts and malevolent entities highlights the ancient Egyptians’ deep-seated reverence for divine guardianship and protection, a theme resonant in many ancient cultures but uniquely personified in Shed’s enigmatic persona.
| Origin | Ancient Egyptian Mythology |
| Deity Type | Solar Deity |
| Appearance | Often depicted as a youthful deity with a curly hair or a crown of the sun disk |
| Role | Associated with the concept of sunlight, radiance, and royal power |
| Symbolism | Symbolized the sun’s life-giving and protective qualities |
| Worship | Shed was occasionally venerated in ancient Egypt, particularly during the Middle Kingdom |
| Cultural Context | Reflected in the solar aspects of Egyptian religion and royal iconography |
1. Historical Context and Origins
Shed’s Historical Background
Shed’s emergence in Egyptian mythology is relatively later compared to other deities, gaining prominence during the New Kingdom period. This era, marked by prosperity and the expansion of both territory and religious ideas, saw Shed rise as a figure of personal protection. Unlike major gods associated with state religion, Shed was more intimately connected with the individual, often depicted in amulets and personal items, indicating his role as a personal guardian.
The Era of Egyptian Mythology and Shed’s Emergence
The New Kingdom, spanning from around 1570 to 1070 BCE, was a transformative period in Egyptian history. It was during this time that Shed’s presence became increasingly notable. His emergence aligns with the period’s heightened emphasis on personal piety and individual interaction with the divine, a shift from the traditional collective religious practices.
Cultural and Religious Significance of Savior Deities
In ancient Egyptian culture, the concept of a savior deity like Shed was pivotal. These figures were not just part of religious practices but were deeply embedded in the daily life and personal beliefs of the people. Shed, in particular, embodied the Egyptians’ desire for personal protection against tangible and mystical threats. His role as a savior deity reflected a broader cultural and religious evolution towards more personalized forms of worship and divine interaction.
2. Iconography and Symbolism
Shed’s Iconography
Shed’s iconography is distinct and deeply symbolic. Often depicted as a young prince, he is shown wearing a crown, sometimes adorned with feathers, signifying his royal stature and divine nature. Another common portrayal is that of a hunter, equipped with a bow and arrow, symbolizing his role as a protector against dangers. These images of Shed, found on amulets and in temple carvings, encapsulate his dual role as a divine guardian and a youthful warrior.
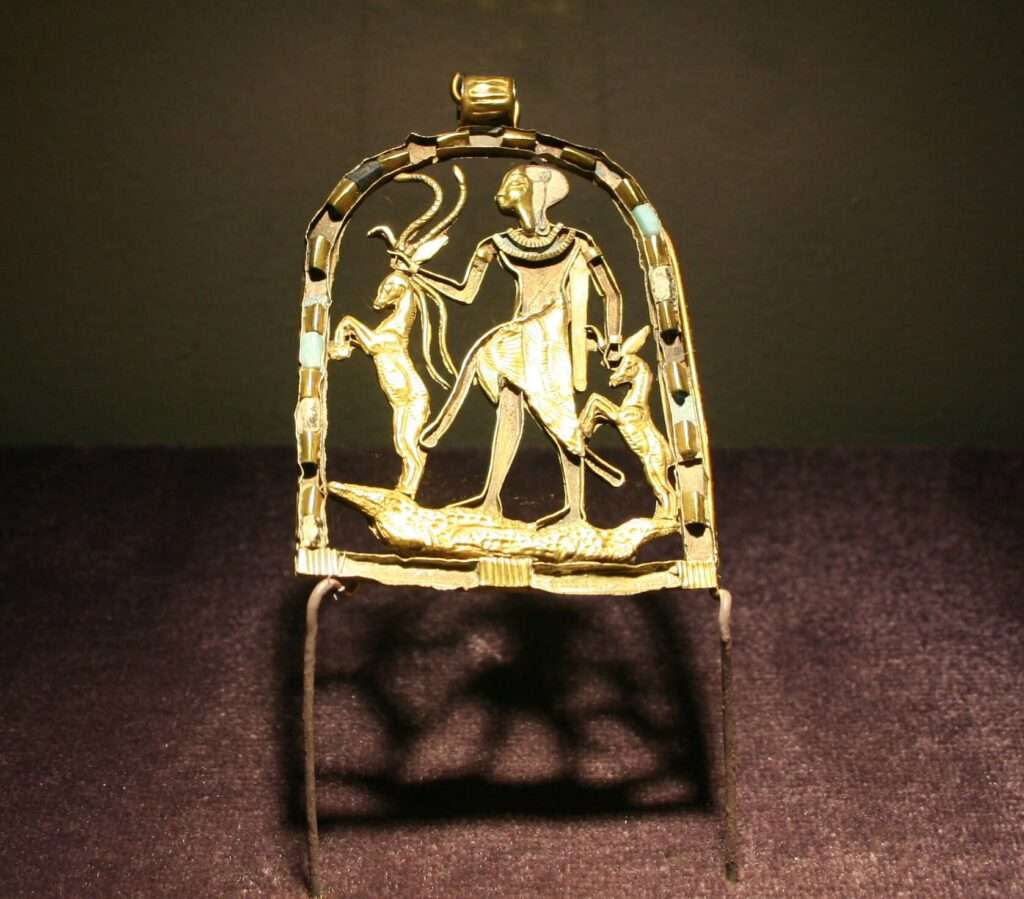

Symbols Associated with Shed and Their Meanings
The symbols associated with Shed are rich in meaning:
- The Crown: Represents divine authority and protection. Its unique style in Shed’s imagery sets him apart as a deity of safeguarding.
- Bow and Arrow: Emblematic of Shed’s role as a hunter, these tools symbolize his active defense against evil forces, reinforcing his persona as a savior.
- Animals: Often seen combating dangerous animals, these scenes highlight his protective nature against physical and spiritual threats.
Comparative Analysis with Other Deities
Shed’s iconography and symbols contrast with other Egyptian deities. For instance, while Horus is also depicted as a falcon or a falcon-headed man, symbolizing the sky and kingship, Shed’s imagery is more grounded, focusing on personal protection rather than cosmic or royal authority. This comparison underscores Shed’s unique position in the Egyptian pantheon as a personal guardian deity, a role less emphasized in the depictions of other gods.
3. Shed in Ancient Egyptian Religion and Culture
Worship and Reverence of Shed
The worship of Shed was a deeply personal practice in ancient Egypt. Unlike the state-endorsed worship of major deities, devotion to Shed was more individualistic. People often invoked Shed for personal protection through prayers and amulets. These amulets, bearing his likeness, were commonly worn for safeguarding against everyday dangers, illustrating the personal nature of his worship.

Temples, Artifacts, and Inscriptions
While there are no known temples exclusively dedicated to Shed, his presence is felt in smaller shrines and household altars. Artifacts such as amulets, jewelry, and small figurines found in both royal and common graves depict Shed, emphasizing his widespread veneration across different social classes. Inscriptions and hymns dedicated to him, although less prevalent than those for major gods, further attest to his importance in daily life.
Rituals and Festivals
Unlike major deities, there were no large-scale festivals or state-sponsored rituals for Shed. Instead, his worship was more intimate, often involving personal rituals performed at home. These practices might have included offering prayers, lighting incense, or wearing amulets bearing his image, especially during travel or in times of danger. This personal mode of veneration highlights the distinctive place Shed held in the hearts and minds of the ancient Egyptians.
4. Shed’s Influence and Legacy
Shed’s Role and Influence in Ancient Egyptian Religion
Influence of Shed in ancient Egyptian religion was significant, especially in the context of personal piety. He represented a more accessible form of divine protection, a contrast to the grandeur of major deities. This accessibility made him particularly influential among common people. His role as a protector against everyday dangers resonated deeply, illustrating a more intimate and personal aspect of Egyptian spirituality.

Transformation of Shed’s Image and Attributes
Over time, Shed’s image and attributes underwent a transformation. Initially revered as a youthful savior, his imagery later merged with other protective deities, such as Horus and Ra, reflecting a syncretism common in Egyptian religion. This assimilation of characteristics from other gods enhanced Shed’s protective qualities, making him a composite deity embodying various aspects of safeguarding and strength.
Shed’s Legacy in Modern Interpretations
In modern times, Shed’s legacy continues to intrigue scholars and enthusiasts of Egyptian mythology. While not as widely recognized as other Egyptian gods, his unique role as a personal savior deity offers a different perspective on ancient Egyptian religious practices. Contemporary interpretations often focus on his symbolism as a protector, resonating with modern themes of guardianship and personal spiritual journey. This continued interest in Shed highlights the enduring relevance of ancient mythological figures in understanding historical cultures and their belief systems.
5. Comparative Mythology
Comparative Analysis with Other Savior Figures
Shed’s role as a savior deity in Egyptian mythology invites comparisons with similar figures in other cultural mythologies. For instance, in Greek mythology, Apollo, also associated with youth and protection, shares similarities with Shed. Both deities are depicted as young and powerful protectors, though Apollo’s domain extends to arts and prophecy, unlike Shed’s more focused role in personal protection.

Common Themes in Savior Deities
Across various cultures, savior deities often share common themes, such as protection, guardianship, and a connection with the youthful or the divine. These themes reflect a universal human desire for protection against the unknown and the assurance of divine guardianship. Like Shed, many of these deities are intimately connected with their followers, serving as personal guardians rather than distant, omnipotent figures.
Divergences in the Portrayal of Savior Deities
Despite common themes, there are notable divergences in how different cultures portray their savior deities. For example, in Hindu mythology, Krishna, while also a protector, embodies a broader spectrum of qualities, including love, wisdom, and playfulness, which are less pronounced in Shed’s portrayal. These differences highlight the unique cultural contexts and spiritual philosophies that shape the depiction of savior figures in various mythologies.
6. Modern Relevance and Interpretations
Shed’s Symbolism in Today’s Context
In the modern world, Shed’s symbolism retains its relevance, particularly in the context of personal protection and overcoming challenges. The ancient Egyptian understanding of Shed as a guardian against physical and spiritual dangers resonates with contemporary themes of resilience and safeguarding against life’s uncertainties. Shed’s portrayal as a youthful protector also echoes in modern narratives that emphasize the power and potential of youth in confronting and overcoming adversities.
Modern Depictions of Shed
In contemporary literature, art, and media, Shed’s imagery is occasionally explored, though he is less prominent than more famous Egyptian deities. When depicted, he often embodies themes of guardianship and protection. In literature, Shed may appear as a symbol or a reference point for characters seeking strength or protection. Modern interpretations of Shed’s iconography blend ancient symbolism with contemporary styles, reflecting the enduring influence of Egyptian mythology. In media, while not a mainstream figure, Shed sometimes features in works exploring Egyptian mythology, serving as a bridge between ancient beliefs and modern interpretations of myth and protection.
7. Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of Shed, the ancient Egyptian savior deity, we’ve uncovered key insights into his role and significance. Shed stands out in Egyptian mythology for his unique representation of personal protection, embodying the human desire for safety and guardianship. His evolution from a youthful figure to a syncretic deity highlights the dynamic nature of religious beliefs. Reflecting on Shed’s story and symbolism underscores the broader importance of understanding ancient mythologies. They offer not just a window into the past but also enduring lessons and themes that continue to resonate in the modern world. In studying figures like Shed, we gain a deeper appreciation of our shared human heritage and the timeless narratives that continue to shape our cultural and spiritual understanding.
