Norse mythology, a rich tapestry of tales and legends from ancient Scandinavia, stands as a cornerstone of cultural heritage, resonating through the ages with its vibrant pantheon of gods, heroes, and mythical creatures. Among these legendary figures is Sigmund, a central character in the Völsunga saga, whose life embodies the quintessential Norse virtues of bravery, strength, and destiny. His tale, interwoven with themes of fate, revenge, and heroism, not only captivates the imagination but also offers a window into the values and beliefs of the Norse people. Sigmund’s story, from his divine lineage to his fateful sword, Gram, unfolds a saga that has influenced countless tales and continues to inspire modern narratives. His legacy in Norse lore is a testament to the enduring power of these ancient myths in shaping our understanding of history, culture, and human nature.
| Attribute | Sigmund Information |
|---|---|
| Origin | Norse Mythology and Germanic Sagas |
| Heroic Figure | Legendary hero and son of Völsung |
| Sword Gram | Wielded the sword Gram (Balmung), a renowned weapon |
| Saga | Central figure in the Völsunga Saga, a significant Old Norse saga |
| Family Legacy | Father of Sigurd (Siegfried), who slayed the dragon Fafnir |
| Cultural Impact | Revered as a symbol of heroism and noble lineage in Norse and Germanic tales |
| Depictions | Featured prominently in the Völsunga Saga, known for his heroic exploits |
1. The Mythical Origins of Sigmund
Sigmund’s Birth and Lineage
Sigmund’s story begins with his extraordinary birth, rooted in the divine and heroic lineage of the Völsung family. He was the son of Völsung, the eponymous hero of the saga, and a grandson of the god Odin, which bestowed upon him a status blending the mortal and the divine. This lineage set the stage for Sigmund’s destiny, intertwining his life with the fates of gods and men. His birth was marked by remarkable omens, foretelling a life of greatness and strife, deeply intertwined with the capricious will of the gods.
Significance in the Völsunga Saga
In the Völsunga saga, Sigmund stands as a central figure, embodying the archetypal Norse hero. His life is a series of challenges and triumphs, from avenging his father’s death to acquiring the magical sword Gram, which Odin himself plunged into the tree Barnstokkr, available only to one worthy of its power. Sigmund’s exploits within the saga are pivotal, driving the narrative forward and setting the stage for the subsequent generations of heroes, including his renowned son, Sigurd.

Mythological Themes and Motifs
Sigmund’s life is rich with themes and motifs central to Norse mythology. His character embodies the struggle against fate, a common thread in Norse tales, where even the mightiest heroes are subject to the whims of destiny. His journey reflects the Norse belief in the interconnectedness of the divine and mortal realms, where gods frequently intervene in the lives of men. Moreover, Sigmund’s story is steeped in the idea of legacy and the enduring impact of one’s actions on future generations, a motif that resonates deeply in Norse lore. His saga, filled with trials, triumphs, and tragedies, encapsulates the complex relationship between fate, free will, and the heroic ideal in Norse mythology.
2. Sigmund’s Legendary Exploits
Heroic Deeds of Sigmund
Sigmund’s saga is a chronicle of heroic feats, marked by extraordinary strength and bravery. His most notable deed was the retrieval of the sword Gram. This legendary weapon, embedded in an ancestral tree by Odin, could only be drawn by a true hero. Sigmund, proving his worthiness, drew the sword, signifying his divine favor and destined greatness. His adventures also include battles against dragons and other formidable foes, showcasing his prowess as a warrior. One such tale recounts his victorious single combat against the dragon Lyngvi, avenging his father’s death and reclaiming his family’s honor.
Key Battles and Adventures
Sigmund’s life was punctuated by numerous battles, both against mortal enemies and supernatural beings. His most significant battles often had larger implications, involving family feuds, quests for power, and divine interventions. In these conflicts, Sigmund demonstrated not only physical strength but also tactical acumen, often outsmarting his adversaries. His adventures extended beyond the battlefield, involving quests that tested his courage, wisdom, and moral judgment.
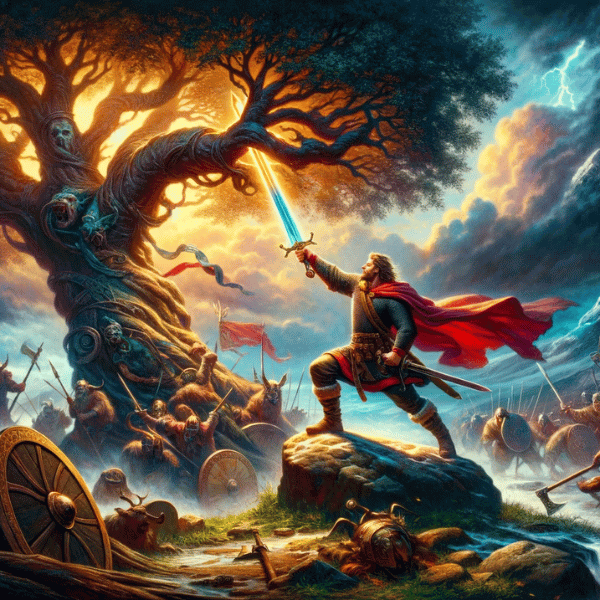

Relationships with Mythological Figures
Sigmund’s interactions with other figures in Norse mythology were complex and multifaceted. His relationship with Odin, his grandfather, was particularly significant. Odin, often a guide and a manipulator in Norse myths, played a crucial role in Sigmund’s life, offering assistance at key moments but also ensuring that his fate unfolded as predestined. Sigmund’s relationships with his family members, including his wife Hjördis and his son Sigurd, are central to his saga. These relationships are characterized by loyalty, love, and sometimes tragedy, adding depth to his character and highlighting the human aspects of his mythical existence.
3. Symbolism and Interpretation
Symbolic Meanings in Sigmund’s Saga
Sigmund’s actions and destiny in Norse mythology are rich with symbolic meanings. His life, particularly his interaction with the sword Gram, symbolizes the concept of destined greatness and the intertwining of human actions with divine will. This sword, granted by Odin, represents not only physical power but also the burden of destiny that Sigmund carries. His trials and tribulations reflect the Norse belief in the inevitability of fate, where even the mightiest can be subject to the whims of the gods. Additionally, Sigmund’s relentless pursuit of vengeance and justice, despite overwhelming odds, symbolizes the Norse virtues of honor and perseverance in the face of adversity.
Universal Themes Across Mythologies
Sigmund’s character shares similarities with heroes from various mythological traditions, highlighting universal themes in hero myths. Like the Greek hero Hercules, Sigmund is born of divine lineage and faces a series of arduous tasks and challenges. Both heroes exhibit extraordinary strength and face trials that test their character and resolve. These similarities underscore common themes in world mythologies, such as the hero’s journey, the struggle against fate, and the quest for identity and purpose in a world governed by higher powers.
Modern Interpretations of Sigmund
In modern contexts, experts interpret Sigmund’s character as more than a mythical figure; they see him as an archetype representing timeless human struggles. They view his journey as a metaphor for the individual’s quest for self-discovery and fulfillment in a world where external forces often dictate terms. Modern interpretations also focus on the psychological aspects of his character, examining his motivations, conflicts, and the impact of his divine lineage on his human experiences. In contemporary literature and media, Sigmund’s character has been adapted to reflect contemporary issues, such as the search for identity and the conflict between personal desires and societal expectations.
4. Sigmund in Art and Culture
Portrayal in Art and Literature
Sigmund’s legend has been a source of inspiration in art and literature for centuries.Classical art has depicted his story in various forms, ranging from intricate carvings on runestones to detailed illustrations in medieval manuscripts. In literature, the epic poems of the Norse Eddas and the Völsunga saga have explored Sigmund’s tale, fleshing out his character with rich narrative detail. Modern literature has also referenced his story, with authors drawing parallels between his mythical struggles and contemporary themes.
Adaptation Over Time
Over the centuries, the legend of Sigmund has evolved, mirroring changing cultural and social contexts in which storytellers retell it. In the medieval period, people often used his story to symbolize noble lineage and heroic virtue. During the Romantic era, writers revisited Sigmund’s saga, emphasizing the tragic and heroic aspects of his life. In contemporary times, various media have adapted his story, including film, television, and video games, often with a focus on the fantastical elements of Norse mythology.
Gallery of Artistic Representations
The enduring appeal of Sigmund’s story is evident in the diverse range of artistic representations it has inspired. These include:
- Medieval Runestones: Carvings depicting scenes from Sigmund’s saga, highlighting the cultural importance of his story in the Norse world.
- Illuminated Manuscripts: Detailed illustrations from the Völsunga saga, showcasing the artistry of medieval scribes.
- Romantic Paintings: Artistic interpretations from the 19th century, emphasizing the dramatic and heroic aspects of Sigmund’s story.
- Modern Artworks: Contemporary artistic renditions that reinterpret Sigmund’s legend in modern contexts, reflecting contemporary artistic trends and interpretations.
5. Historical Perspectives
Archaeological Evidence and Historical Context
The legend of Sigmund, like many Norse myths, is steeped in a blend of historical fact and mythological fiction. Archaeological discoveries have provided some support for the historical context in which these stories were told. Artifacts such as weapons, runestones, and burial sites from the Viking Age offer glimpses into the world that inspired these tales. For instance, the discovery of swords from the era, similar to the legendary Gram, suggests a historical basis for the symbolic significance of swords in Norse culture. Additionally, the depictions of warriors and battles in Norse art align with the descriptions of heroic exploits found in sagas like that of Sigmund.

Expert Opinions on Myth and History Interplay
Experts in Norse mythology and history often discuss the intricate interplay between myth and historical fact in sagas. They suggest that while characters like Sigmund may not have existed in the literal sense, their stories are grounded in the realities of the Norse world. These sagas served multiple purposes: preserving history, imparting moral lessons, and explaining the world through the lens of Norse spirituality and belief systems. Scholars argue that figures like Sigmund likely represent a composite of real-life warriors and kings, their deeds amplified and embellished over generations of storytelling.
6. Conclusion
Sigmund’s saga, a compelling blend of divine fate and human valor, has left an indelible mark on Norse mythology and culture. His story, woven with themes of heroism, destiny, and the intertwining of the mortal and divine realms, encapsulates the essence of Norse lore. Sigmund’s enduring legacy in art, literature, and modern media underscores the timeless relevance of these ancient tales. They continue to resonate, offering profound insights into the human condition and the cultural heritage of the Norse people. Through the saga of Sigmund, Norse mythology remains a vibrant, living tapestry, rich in lessons and symbolism, reflecting the universal quest for meaning, purpose, and understanding in the tapestry of human history.
